|
Runtime refactoring
|
In order to make the Eclipse runtime more flexible and allow independent use of runtime components, the org.eclipse.core.runtime plug-in has been split into several plug-ins:
-
org.eclipse.equinox.common - common code used by more than one piece of the former runtime plug-in (i.e. IPath, IStatus, IProgressMonitor).
-
org.eclipse.equinox.registry - Extension registry
-
org.eclipse.equinox.preferences - Preferences mechanism
-
org.eclipse.core.jobs - Jobs mechanism
-
org.eclipse.core.contenttype - Content mechanism
-
org.eclipse.equinox.supplement - A supplemental "plug-in" that is used to support running without OSGi.
New APIs were added to facilitate control of the split runtime pieces.
The runtime refactoring should be transparent to other plug-ins. For more details, see the Eclipse 3.2 migration guide.
|
|
Common navigator
|
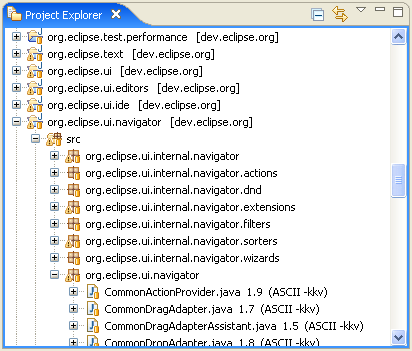
A new plug-in, org.eclipse.ui.navigator, introduces a framework for building viewers that combine content from multiple domain models. The framework allows declarative contribution of content, labels, actions, filters, and other capabilities. The org.eclipse.ui.navigator.resources plug-in provides a concrete use of this framework in the form of a Project Explorer view, and declarative viewer extensions for the IResource model.
|
|
Tabbed properties framework
|
A tabbed properties framework has been added. The tabbed properties framework provides a replacement property sheet page, allowing properties to be shown in the Properties view using arbitrary controls, organized by tabs and sections that are contributed via the extension registry.
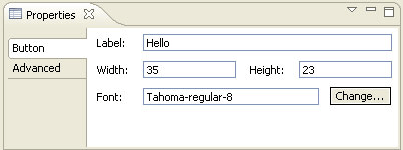
See the article The Eclipse Tabbed Properties View for details. |
|
File system API
|
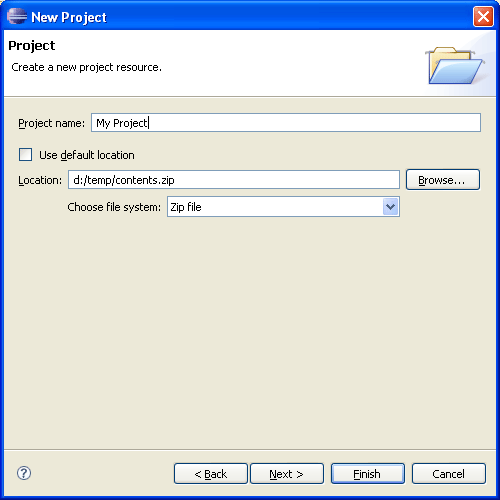
A new plug-in, org.eclipse.core.filesystem, introduces a new generic API for interacting with file systems. The platform has been migrated to use this file system API rather than java.io APIs. This means resources can be created in arbitrary backing file systems, and plug-ins can provide support new kinds of file systems.
Support has been added to the project and linked resource wizards for creating resources that are linked to other file systems. Plug-ins that define alternate file systems can hook into this wizard support by using the org.eclipse.ui.ide.filesystemSupport extension point.
|
|
Categorization added to Import and Export
|
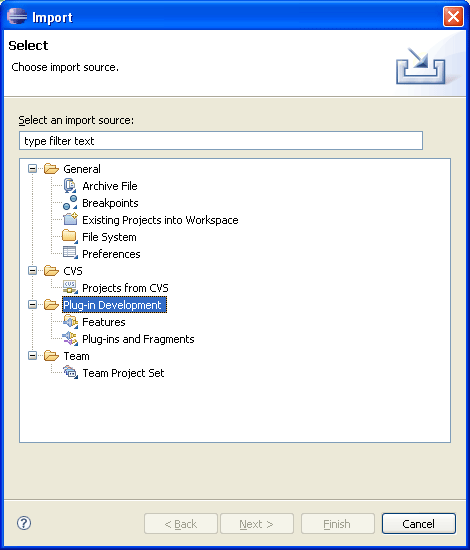
The org.eclipse.ui.importWizards and org.eclipse.ui.exportWizards extension points now support categorization.
|
|
Tooltips for annotations in Text editors
|
Annotation hovering has been pushed down from JDT Text to Platform Text. Text, vertical and overview ruler hover support is installed by TextSourceViewerConfiguration which is used by text editors:

|
|
Annotation navigation in Text editors
|
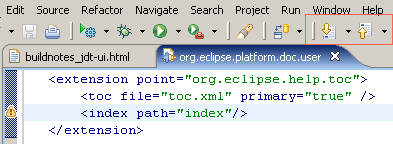
Annotation navigation has been pushed down from JDT Text to Platform Text and is now available in all text editors:
|
|
JFace field assistance
|
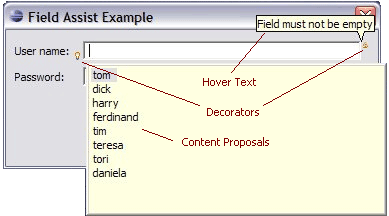
JFace introduces new support for assisting the user in completing fields inside dialogs and forms. The org.eclipse.jface.fieldassist package provides classes that let you decorate arbitrary controls with images and corresponding hover text. These can be used for purposes such as marking required fields in a dialog, showing field-based error conditions, or showing content-assist prompts. The package also allows you to install content proposals on a control, including a pop-up dialog with content proposals, secondary pop-ups for further information, and options for invoking proposals explicitly or in an automatic (type-ahead) style.
|
|
JFace TreeViewer enhancements
|
AbstractTreeViewer now supports multiple equal elements in the tree, each with a different parent chain. This support requires that clients enable the element map by calling setUseHashLookup(true).
TreeViewer now supports SWT.VIRTUAL trees. There is a corresponding lazy content provider ILazyTreeContentProvider that only returns contents as they are needed.
|
|
Support for dynamic Help content
|
Help system now supports dynamic composition of help content. Topics authored in XHMTL can contain additional Eclipse-specific markup for on-the-fly filtering of content based on os/ws/arch values, presence of plug-ins, enabled capabilities, etc. Shared content can be included into multiple documents. Finally, plug-ins can contribute XHTML fragments that plug into anchors in other documents. All this now enables information developers to provide dynamic documents that tailor themselves to the context at the time of viewing. |
|
Help search enhancements
|
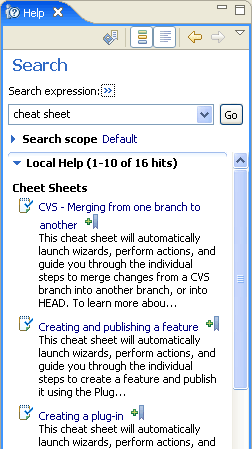
User assistance indexing and searching has been enhanced in various ways. Additional search participants can be registered via extension point that can add content to the Lucene index. Help now contributes an XHTML search participant that can index dynamic help documents authored in XHMTL (see above). In addition, documents that were previously not in the index will now appear (for example, cheat sheets and Welcome pages). Search hits can now have different icons and the 'open' action can be delegated to the search engine.
|
|
Problems can be grouped
|
Problems in the Problems view can now be grouped. There are default groupings by severity and problem type, and additional groups can be defined via the org.eclipse.ui.ide.markerSupport extension point.
|
|
Improved help in dialogs
|
Most dialogs in Eclipse now have a standard help button on the bottom left corner. This button summons context help, same as pressing F1 (on Windows). In addition, the help content will now appear in the dialog's tray instead of in a separate window. Custom dialogs can inherit this functionality by subclassing the new TrayDialog class rather than Dialog. Cheat sheets can also follow you into dialogs (in the tray) for those steps that involve opening dialogs. |
|
Embed command links in User Assistance content
|
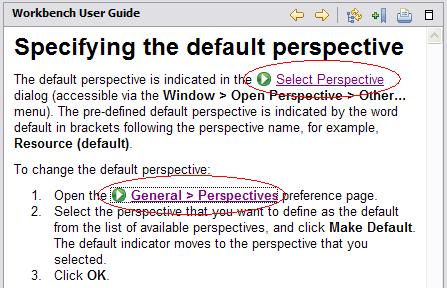
Links in Help, cheat sheets, and Introduction content can now execute commands when activated by the user. Command links can be used to open preference pages, launch wizards, show views, open perspectives and for many other purposes. The command framework is extensible so many more uses of command links are possible. The Workbench User Guide has been enhanced with command links in many places. The picture below shows two command links in a help topic:
|
|
Support for launching commands from cheat sheets
|
Commands can now be launched from cheat sheets. The content file below contains commands to open the Search view and Package Explorer. <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><cheatsheet title="Example of Commands in a Cheat Sheet">
<intro>
<description>A cheat sheet shows the
package explorer</description></intro><item title="Show Search View">
<description>This is a step with a command
which shows the search view.</description><command serialization=
"org.eclipse.search.ui.views.SearchView"/></item><item title="Step 2">
<description>This is a step with a command and
parameters, shows package explorer.</description><command serialization="org.eclipse.ui.views.showView(
org.eclipse.ui.views.showView.viewId=
org.eclipse.jdt.ui.PackageExplorer)"/> <onCompletion>
Command example completed.
</onCompletion></item></cheatsheet> |
|
Composite cheat sheets
|
Composite cheat sheets are new for Eclipse 3.2. A composite cheat sheet provides guidance for a large problem by dividing it into smaller tasks each of which has its own cheat sheet. Tasks can be organized into groups. Composite cheat sheets open in the cheat sheet view and are launched using the cheat sheet selection dialog. Each task has a description, hyperlinks direct the user through a sequence of tasks.

Composite cheat sheets have a tree which shows the tasks and their status. The right hand/lower panel contains the individual tasks. 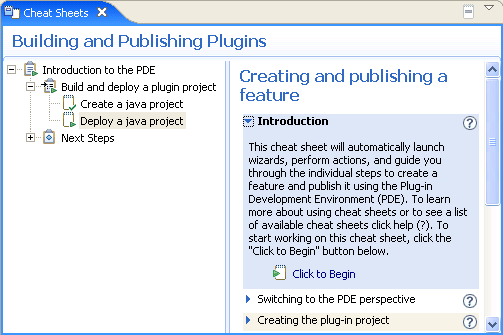
The content of a composite cheat sheets is defined in an XML file. The content file can specify what dependencies exist between tasks so that a task can only be started after any prerequisite tasks have been completed. |
|
Help keyword index
|
Help now has a keyword index, where you can register keywords from your documentation and supply a link to an appropriate help document. The index is available in both the Help view and Help window (view shown below).

|
|
XHTML help docs conversion tool
|
PDE has a new utility to quickly convert a plug-in's HTML help documents to XHTML. In addition to converting the HTML to valid XHTML, the tool will update the filename extension, the table of contents, and add the necessary bindings to enable dynamic content and searching of the XHTML content. After this conversion, users can take advantage of the new 3.2 Help features such as dynamic content filtering, content reuse, and dynamic content contribution that all require XHTML as the content format.
This function can be invoked via PDE Tools > Convert Help files to XHTML from the context menu of plug-in projects. 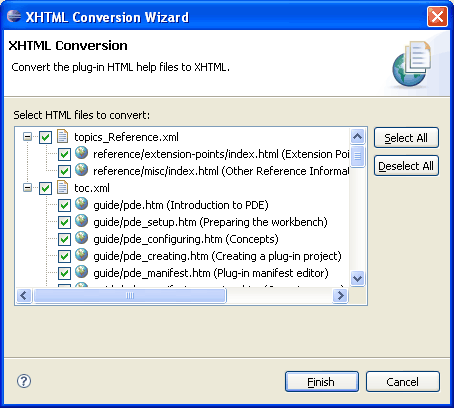
|
|
Universal welcome
|
Based on our experience with concrete Welcome implementations, we now offer a configurable Universal Welcome to be used by any product. Products can choose between 7 predefined main sections: Overview, First Steps, Tutorials, Samples, What's New, Web Resources, and Migrate (Eclipse SDK uses 4 of them). Universal Welcome has configurable page layouts and importance levels for each contribution, and is fully theme-aware. It also offers both HTML and SWT presentations for 100% platform coverage.
A Welcome preference page provided by Universal Welcome opens up Welcome customization to the end users, and can be included in any product that wants to offer it. You can read more about this in the Universal Welcome specification. 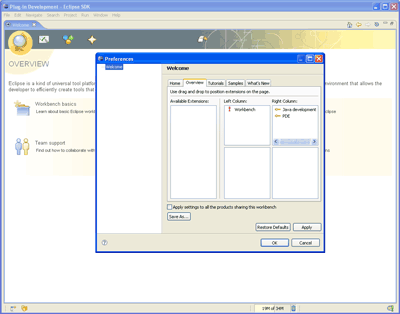
|
|
Support for configuration and themes in Welcome
|
The Intro framework has more configurability support. An intro configurer can be contributed that offers one-time computation of the group children, variable substitution support, and late anchor path resolution. This support is heavily used by Universal Welcome but can also be used by other Welcome implementations.
Themes represent named collections of CSS files, properties, and images that collectively define the look of the Welcome content. Universal Welcome takes advantage of this support by providing theme selection capability and two concrete themes in 3.2: 'Circles' and 'Purple Mesh'. 
|
|
Namespace support for the Ant extension points
|
The org.eclipse.ant.coreantTasks and antTypes extension points now allow for the designation of a URI that the definition should live in. See bug 133190 for full details of all the changes.
|
|
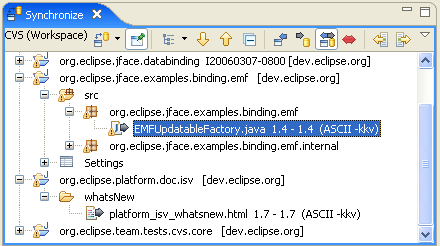
Team support for logical model integration
|
API has been added that allows logical models to participate in Team operation. With this API, Team providers can:
- Consult models to ensure all required resources are included in a Team operation.
- Use model semantics to aid in resolving merge conflicts.
- Allow models to participate in the display of resources during Team Operations
|
|
Sort indicator in tables and trees
|
Table and Tree now support a sort direction indicator in the header of the column.
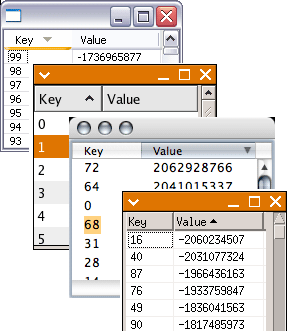
SWT snippets showing sorting by column (simple) and sorting by column (virtual table).
|
|
Reorderable columns in trees
|
In Eclipse 3.1, we added the ability to reorder columns in a Table. That support has now been added to Tree.
The display order of columns in a tree can be changed by dragging the column header, or it can be set programmatically.
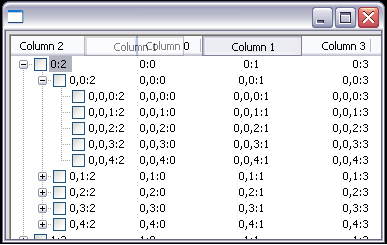
Example snippet.
|
|
Improved XP theme support
|
On Windows XP, SWT now shows the textured background in tab folders. The groups, labels, check boxes, etc. are all transparent to this background. Also, custom widgets, such as StyledText, now show the correct border for the prevailing Windows XP theme.
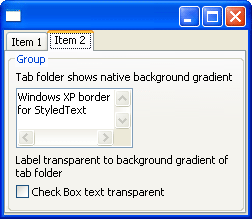
See the SWT FAQ for instructions on how to run with a Windows XP skin.
|
|
Animated GIFs
|
Animated GIF images can be saved to file.

For an example see the SWT snippet.
|
|
Desktop appearance notification
|
When appearance settings such as theme, font, or default colors are changed for the desktop, an SWT.Settings event is issued for the Display.
|
|
Dispose notification
|
Previously, when an SWT.Dispose event was received for a parent composite, all the children were disposed and therefore could not be referenced. For 3.2, the Dispose event is received before the children have been released in the OS.
|
|
Tool tips for columns
|
Tooltip text can be set on a table or tree column header using TableColumn/TreeColumn.setTooltipText(String).
|
|
Vertical CoolBar
|
A vertical coolbar can be created by using the SWT.VERTICAL style.

|
|
OpenGL support
|
You can now use OpenGL in SWT applications. The OpenGL interface works with third-party OpenGL libraries such as LWJGL.
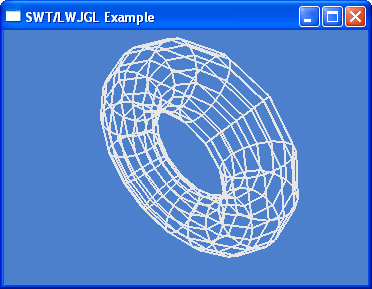
For examples, see the SWT snippets
|
|
Virtual tree
|
Tree now supports the SWT.VIRTUAL style. This allows you to create trees with large amounts of data quickly. When TreeItems are needed, they are created on-demand.
For an example see the SWT snippet.
|
|
Buttons with image and text
|
Buttons can now show an image as well as text. This feature is supported on Windows XP, Mac OS X, and GTK.
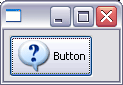
|
|
HIView on Mac OS X
|
SWT now makes use of HIView on Mac OS X. This resolves many clipping and sizing issues.
|
|
Embedding objects in text
|
Using TextLayout and StyledText, it is now possible to embed objects such as images or widgets inside text. Glyph metrics such as ascent, descent and width can be specified. Objects wrap with the text.
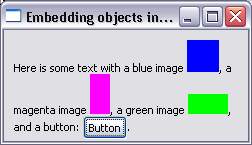
For examples, see the following snippets:
|
|
Indent, align and justify text
|
TextLayout and StyledText now support indenting, justifying, and aligning text.

For examples, see the following snippets:
|
|
Text baseline rise
|
Using TextLayout and TextStyle, it is now possible to specify the baseline rise for a range of text.
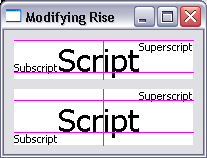
For an example see the SWT snippet.
|
|
HSB color support
|
A color can be created by specifying the hue, saturation, and brightness. In addition, for a given color, the hue, saturation, and brightness values can be queried.
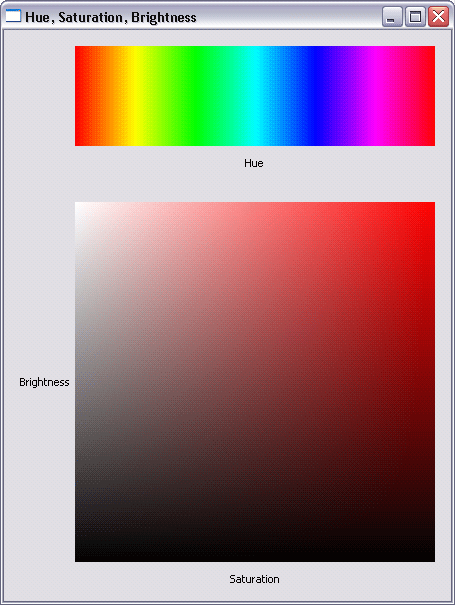
For an example, see the SWT snippet
|
|
Background image
|
A background image can be set into a control. In addition, the background can be inherited by child widgets such as labels.
For an example, see the SWT snippet
|
|
Native image loading
|
The constructor Image(Device device, String filename) will now load images using native operating system calls. This has improved performance of image loading and increased the maximum size of image that can be loaded.
|
|
Dragging text
|
If the SWT.DragDetect event is hooked on Text or StyledText, the selection will not be cleared when the user drags from within a selected range of text. This makes it possible to support dragging from the Text and StyledText widgets.
For an example, see this SWT snippet
|
|
New ExpandBar widget
|
The ExpandBar widget allows the user to show and hide collections of widgets by clicking on a header. The ExpandBar contains multiple items which each may have an image and title in the header.
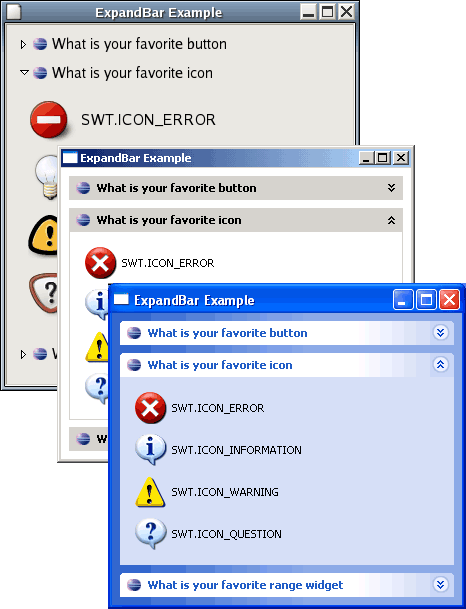
For an example, see this SWT snippet.
|
|
Bullets in StyledText
|
StyledText can now show lists formatted in a variety of styles, including bullets, numbered, upper case or lower case letters, and custom-defined styles.
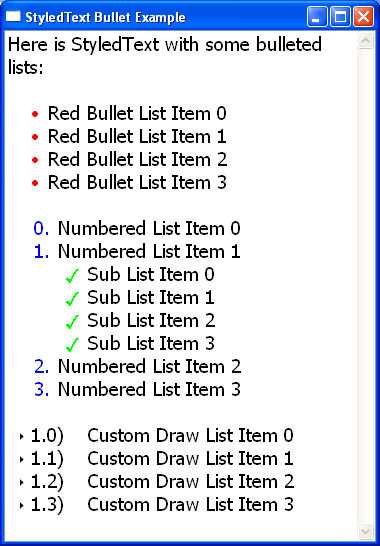
For an example, see this SWT snippet.
|
|
Custom draw Tree
|
The Tree widget now supports custom draw for individual cells. Applications can enhance the native look and feel of the tree by custom rendering of the data. The application has control over row height so multiple lines of text can be drawn. In addition, it can present multiple images in the same cell, change font or color multiple times, and change the way selections are drawn.
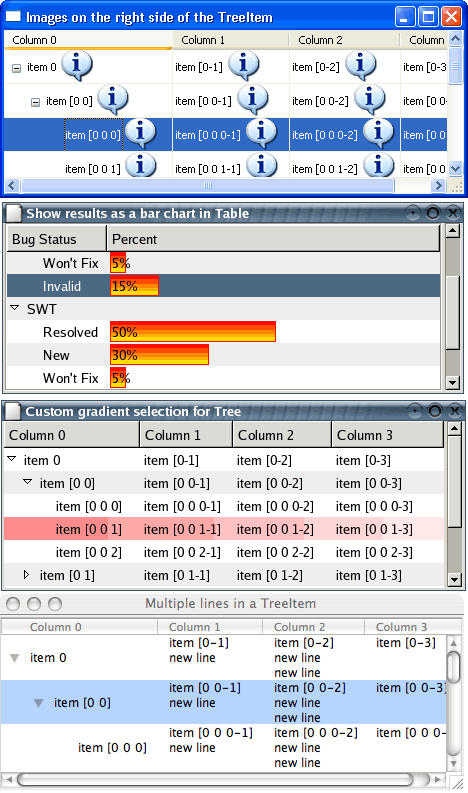
For examples, see the following snippets:
|
|
Custom draw Table
|
The Table widget now supports custom draw for individual cells. While still maintaining the native look and feel of the table, users can customize how cells are drawn to display data in a form other than text with an image, to show multiple lines of text in one cell, to change font and color multiple times within the same cell, to override the native selection drawing, etc.
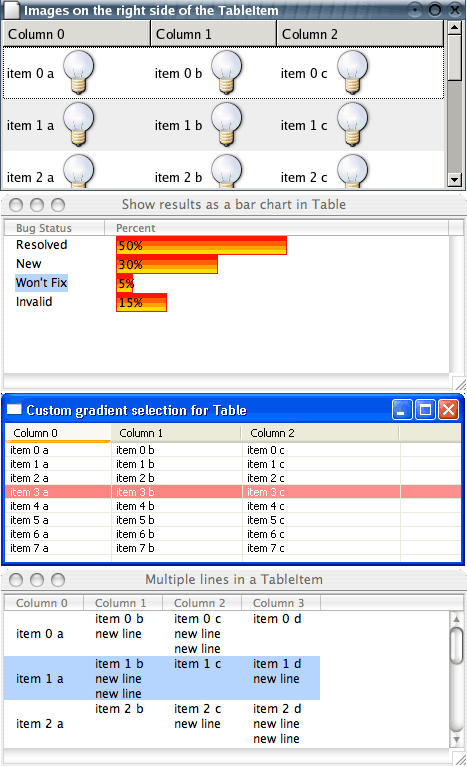
For examples, see the following snippets:
|
|
Drag over effects for Table and Tree
|
The Table and Tree widgets now provide visual feedback of what is being dragged.
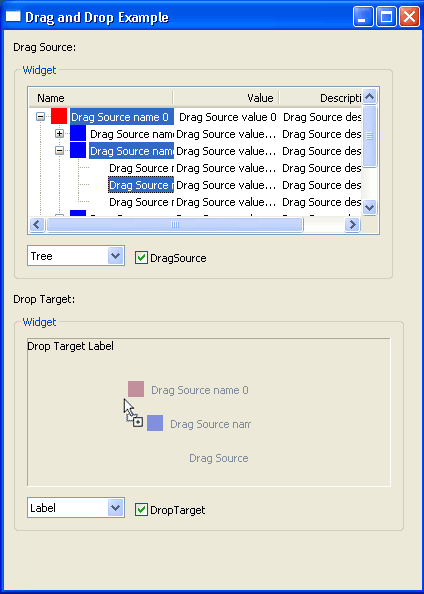
|
|
New Tooltip class
|
The new ToolTip class can be used to display tooltips that are not directly tied to a Control. These tooltips can be placed anywhere, and can have either the platform default appearance or a BALLOON appearance as shown below.

|